More greenhouse gases were produced in 2018 than any previous year, despite more than 20 countries reducing their carbon emissions since 2000, research from UNSW Sydney and collaborators has shown.
And while the COVID-19 pandemic may have brought about a temporary reprieve in relation to carbon emissions, experts have forecast a return to the previous upward trajectory of greenhouse gas production after observing economic growth moving back to previous levels.
In a study published this week in Environmental Research Letters, the researchers show that road transport, meat consumption and a global trend towards expanding floorspaces – some of the hallmarks of affluent economies – were big factors behind greenhouse gas increases, while industry, agriculture and the energy systems continued to account for a substantial slab of the carbon emissions total.
Professor Tommy Wiedmann from UNSW’s School of Civil and Environmental Engineering was part of a team of 29 researchers from six continents that examined the latest, globally available emissions data for the decade leading up to 2018.
He says the group looked at emissions in 10 regions of the world as well as comparing which sectors in each were responsible for the largest emissions – and which showed the largest growth.
“The main thing we found is that almost everywhere we looked, and in almost every sector, greenhouse gas emissions just kept on rising, right up to the beginning of COVID-19, when we had the highest greenhouse gas emissions we’ve ever had,” Prof. Wiedmann says.
“This is despite the fact there are more than 20 countries that have reduced their emissions. It’s when you take this bird’s eye view of the total emissions that you see that those reductions barely make a difference.”
Prof. Wiedmann says he knew that emissions were still growing, but he was surprised that moves towards renewable energy have not made larger dents in the emissions.
“The results are quite sobering, we just haven’t been able to bend the curve. Yes, we have slowed the growth of emissions a bit when compared to the decade leading up to 2010, but if we want to meet the Paris Agreement target by 2050, then we have to get emissions down really quickly.”

Professor Thomas Wiedmann was part of the 29-member research team that just published the damning findings of a global evaluation of greenhouse gas emissions. Credit: University of New South Wales (UNSW)
Five sectors
The study divided sectors into the five major groups of energy, industry, buildings, transport, and land use. The researchers focused on the trends in these sectors and their underlying components – such as electricity generation, road transport, or livestock emissions – as well as broad drivers like economic growth, population growth, energy efficiency, and carbon intensity of different human activities. They calculated the extent to which each factor had an impact for each sector and world region.
Lead author of the study, researcher Dr William Lamb from Berlin’s Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change, says global greenhouse gas emissions increased by 11 per cent from 2010 to 2018.
“Only a few sectors saw a significant downward trend, such as the energy sector in Europe,” Dr. Lamb says.
“By contrast, climate-damaging coal power generation increased in Asia. And emissions in the transport and building sectors rose in almost all regions of the world – this was in part because people in rich countries are travelling more and more and taking up more and more living space.”
The study also found that global freight travel activity grew by 68 per cent in the last two decades, while the largest emitter overall was the industrial sector, adding the equivalent of 20.1 gigatonnes of CO2 worldwide in 2018, which was 35 per cent of total emissions and 14 per cent more than in 2010.
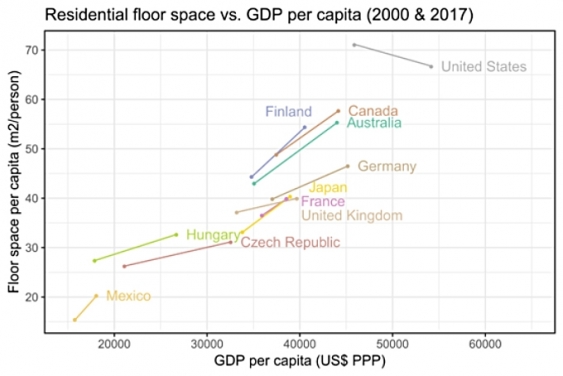
Australia has had one of the steepest rises in floor space per person in the time period examined. Figure: ‘A review of trends and drivers of greenhouse gas emissions by sector from 1990 to 2018.’ Courtesy of UNSW Media.
The trend towards greater floor space area in new buildings was also highlighted as a driver of emissions. With 55 square metres per person in floor space, Australia belongs to the top three countries driving this trend, Prof. Wiedmann adds.
“Looking at the trend towards larger houses in Australia, we’re seeing people spend more of their time indoors and that that drives up energy demand because a larger house needs more cooling or heating.
“You need to fill that house with furniture, with furnishings, with appliances, and so the general level of material consumption is also driving up and it goes hand in hand with greater emissions.
“Of the five sectors that we looked at, buildings was the smallest one with six per cent globally of total emissions. But if you count the electricity used in buildings for heating, cooling, lighting, and allocate this to buildings, then the share goes up to 17 per cent.”
Prof. Wiedmann says an often-overlooked sector responsible for emissions was the land sector, which may be responsible for up to a quarter of climate pollution.
“From 1990 to 2018, humans have shrunk primary forest areas by more than seven million square kilometres, almost as much as the size of Australia,” he says.
“This is often for pasture and cropland in Latin America, Africa and South-East Asia that now produces food for Europe, North America or China.
“Land use emissions are also driven by a ‘westernisation’ of diets, with meat and internationally sourced refined products replacing traditional and seasonal produce.”

Barley harvest in La Pampa, Argentina. Prof. Wiedmann says the land sector may be responsible for up to a quarter of climate pollution: “From 1990 to 2018, humans have shrunk primary forest areas by more than seven million square kilometres, almost as much as the size of Australia,” he says. Credit: Shutterstock
Toward 2050
Prof. Wiedmann says with less than 30 years to go to meet the targets set by the Paris Agreement to achieve net zero emissions, the developed world needs to start limiting its consumption and relaxing its pursuit of affluence.
“Some things will have to change,” he says. “This doesn’t mean we have to go back to the stone age, but we need to work on development that respects ecological limits and leads to more equity in the world.
“The Global North – or developed countries including Australia – should really reduce their material consumption while allowing the Global South – or developing countries – to catch up.”
He says achieving this means government, industry (producers) and individuals need to all pull together towards sustainability.
The three most powerful changes they could make to bring emissions down by 2050 include:
Governments
- Legislate the phasing-out of fossil fuels, support renewable energy
- Tax carbon and over-consumption
- Adopt Wellbeing Economy Alliance principles
Producers
- Follow science-based target reductions of Scope 2 and Scope 3 emissions
- Adopt industrial ecology/circular economy principles
- Achieve maximum energy and material efficiency
Individuals
- Don’t own a car, use public transport or car/ride sharing
- Eat less meat, adopt an 80+ per cent plant-based diet
- Switch to 100 per cent renewable electricity or install solar on own home.
The work, published in Environmental Research Letters, is being used to inform the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which is scheduled for publication in 2022.
Check out the original study here.
This article was published initially on 30 June 2021. It has been republished here courtesy of UNSW Media. View the story on the News section of the UNSW website.
Lead image: Greenhouse gas emission are still at record levels, despite a move toward renewable energy in some parts of the world. Credit: Shutterstock


